Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED)
What's OLED?
Structure
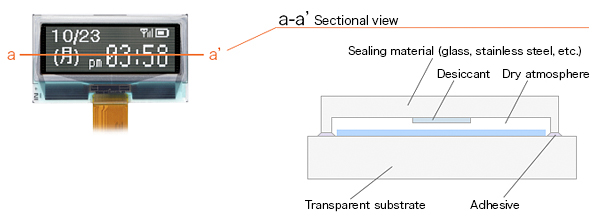
An OLED has a structure which is an arranged organic LED device. It is composed by stacking thin film layers made from organic materials applied between two electrodes on a transparent substrate.
Emission principle
OLED devices operate when the energy, which is generated by carrying electrons and holes away respectively in the functional organic thin film layers, recombine in a light emitting layer. Essentially, this recombination changes energy into the light.

White light emission and color scheme
White light emission
Futaba OLEDs use white light emission formed by the two-color combination of blue and orange light emitting materials.
The chromaticity of white color normally will change over time because the individual emission lifetime for each color is different .
On the other hand, Futaba OLEDs achieves a much longer life time for a white emission with the original stacked OLED layer structure.
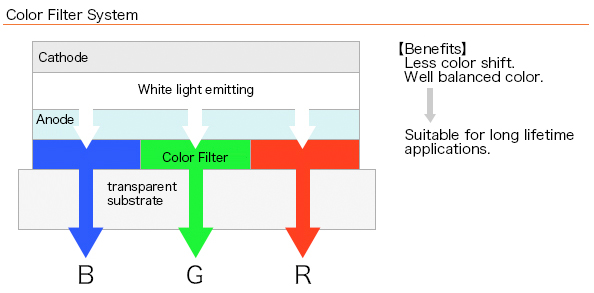
Color filter system
Futaba color OLEDs, combines white organic LED devices which has higher-brightness, longer lifetime with the color filter method. This feature solves the disadvantage of shorter lifetime for the indivdual organic materials of RGB. This is why Futaba OLEDs are used for many products in various fields including automotive applications.